Human Resource Employee Retention Issues
Human Resource Employee Retention Issues
Introduction
Human resources performs its function as a company's unit formed to ensure that personnel are efficient, completely conversant and seriously stimulated. As a matter of fact, the above-mentioned factors can be motivated by specific human resource strategies together with the possible accrediting set of management and communication with employees, which are known to be the major constituents to corroborative employee basis. Retention and turnover are closely connected. Despite the fact that some turnover (the opposite of retention) can provoke businesses to inoculate innovative talents and create new possibilities to the company, basic retention is the major concern for human resources and organization's leadership. Employee retention is a very important issue for human resources. The current paper will investigate the issue of employee retention and define methods to fix and improve this problem.
Employee Retention
Employee retention concerns the capability of a company to retain its workers. Employee retention can be demonstrated by a mere statistics (for instance, a retention ratio of 80 percent typically defines that a company preserved 80 percent of its employees in a selected period of time). Nevertheless, a lot of HR managers believe that employee retention relates to the attempts by which employers try to conserve employees in their personnel. In this case, retention appears to be a strategy rather than a result. The retention of employees does not stand for the fact of hiring an employee who will occupy the same position until he/she retires. In fact, employees require challenges in order to preserve them stimulated; thus, the employer requires work that constantly challenges employees' capacities and competence, and therefore the overall retention should not be complicated. The process of employees' stimulation to strive to occupations with more liability instead of searching for promotion possibilities outside the organization is believed to be the best retention strategy. Possibilities for professional evolvement, consistency projecting and education, which provide employees with assortments for taking on extra liabilities or cross-functional tasks, can enhance retention and lower the overall level of turnover. Thus, employers should concentrate on retaining high-operating employees, but not merely retaining all employees regardless of how they operate, in order to prevent a situation when the organization's turnover is nadir.
Employee retention ratio is a beneficial statistic for an employer to measure. It can be measured as a whole and sporadically as well (for example quarterly or biannually). In fact, the overall formula is simple. It is important to divide the total number of all workers who left the company during a selected period of time by the overall quantity of employees at the end of a selected period in order to get the percentage.
|
Sample Inputs |
Sample Calculation |
|---|---|
|
Period of time: Fourth Quarter |
25– 5 = 20 |
Table 1. Sample employee retention calculation
Typical employee retention ratios range between 70 and 85 percent, but they can greatly differ due to industry or calculation manner. In fact, freewill turnover ratios have lowered recently because of challenging economic circumstances, while redundancy-connected turnover has become more typical. The greatest turnover ratios and the lowest retention standards are usually investigated in retailing, hotels, catering and leisure, call centers, and among other less stipendiary private sector services categories. These levels also differ from region to region. There is a tendency that the greatest turnover ratios and the lowest retention ratios are found in those regions where unemployment is the lowest and where it is comparatively plain for people to insure acceptable disjunctive employment.
The research have demonstrated that spending connected to immediate replacement of an employee might be as high as 50-60 percent of the employee's yearly salary, but the general spending of turnover might become as high as 90-200 percent of the employee's yearly salary. This spending incorporates applicant apprehensions, innovative employment education, enlister's salary, disjunction manipulation, occupation infelicities, departed sales, lowered self-esteem, and a lot of other spending to the company. Turnover also influences company's productive capacity.
Practically all companies measure their levels of retention and turnover. In a number of industries, including retail, customer service, and hospitality overall retain (turnover) rations of 30-40 percent are typical and sometimes even recognized as valid. A number of HR managers believe that it is important to formulate and build the company approximate high-turnover. This allows the companies to ensure that the jobs are easy to learn so that the company will be able to swiftly assimilate new employees. This is believed to be a reality in a lot of organizations, but the facts demonstrate that such a strategy cannot be considered as sound. Regardless of the function they perform, personnel employees have much greater value than workers who are actually "cycling through" the company. A number of researches depict that the overall cost of an employee detriment can range from tens of thousands of dollars to 1.5-2 of annual salary. Therefore, in order to consider the real cost of employee detriment, it is crucial to analyze a number of factors. Firstly, the company will spend resources to hire a new employee, including the costs that will be spent on advertisements, apposition, assessing, and actual hiring. Secondly, the company will spend resources on the process of onboarding a new employee, including education and management time. Thirdly, the company will lose productivity and effectiveness, as it may take a new employee 1-2 years to be able to attain similar efficiency as an existing employee. Fourthly, the company will lose engagement due to the fact that other employees who observe high level of company's turnover will obviously extricate and lose effectiveness. Fifthly, it can provoke numerous errors. In fact, new employees require more time to learn and are frequently less experienced at solving difficult issues. In case of healthcare, this can lead to much higher error ratios, diseases, and other very costly spendings, which are not observed by human resources. Sixthly, the company will spend a lot of costs on. For at least 2-3 years the company will credibly invest 10-20 percent of an employee's salary or even more in education. Seventhly, turnover has serious cultural impacts as when somebody leaves, other employees ask him/her 'why?' and make appropriate conclusions. Finally, it is crucial to remember that people, especially employees, are believed to be "appreciating asset". Therefore, the longer they retain within a company, the more effective and efficient they become as they learn the overall system, they learn the items or products, and they learn how to work together to reach success.
It is important to make a distinction between low-performing employees and best or top executants; thus, the attempts to retain employees should be calibrated at profitable, contributing employees. Employee turnover is believed to be an indication of a huge problem, which has not been solved. This huge problem may incorporate decreased employee self-esteem, destitution of a serene career path, shortage of acknowledgement, low level of employee-manager intercourse or a lot of other difficulties. A shortage of contentment and apprehension to the company can also provoke an employee to repeal and start searching for other possibilities. In fact, payment does not always perform such a great role in entailing turnover as it is usually considered.
In business settings, the major purpose of any employer typically stands for the possibility to lower employee turnover and therefore decrease training spending, enrolment spending, and detriment of talent and organizational knowledge. Implementation of lessons learned from the major organizational conduct concepts allows employers to enhance retention ratios and lower the concurrent spending of high turnover. Nevertheless, this is not always the case. Employers may search for "assertive turnover" when they have an objective to endorse only those employees who they believe to be the best executors.
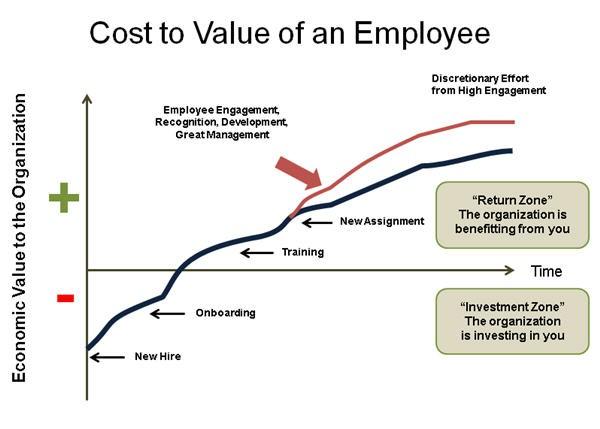
Figure 1. Cost of employee values
The Methods to Improve and Fix Human Resource Employee Retention Issues
There are numerous ways to improve and fix various retention issues. The first method to deal with these issues is to perform employee surveys. In fact, employees' surveying can help companies to gain comprehension of the stimulation, commitment and gratification of their workers. It is crucial for companies to comprehend the prospect of a worker in order to formulate special projects calibrating any specific problem, which can influence employee's retention. The second method concerns exit interviews. Inclusion of exit interviews in the procedure of employee disjunction, companies can achieve valuable understanding of the personnel practice. Exit interviews enable the company to cognize the impulses of the workers' aspiration to dismiss as well as the facets of their labor, which they rejoice. In such case, the company can utilize such data in order to make required alterations to their organization to preserve top capacities. Exit interviews should include questions about the appropriate problems and evoke truthful answers from parting workers to be efficient. The third method to improve or fix human resource employee retention problem concerns the work with employee retention consultants. In fact, an employee retention consultant can help companies in the procedure of preserving the best employees. Consultants may acquire competence on how to ideally define problems connected with turnover in a company. When these problems are defined, a consultant is able to offer projects or various company alterations in order to appeal to such problems and help in the realization of these projects or alterations.
When a company concentrates on the essentials, it is able to go a long way towards creating high-retention personnel. Companies may begin with identifying the culture and defining the kinds of people who would prosper in such kind of environment. Therefore, companies are supposed to follow the essentials, innovative employment focus, and boarding projects. Attraction and recruiting of the best skilled individuals demands time, human resources, and funding. Recruitment is believed to be a very useful tool for retention improvement. When the candidates are presented with practical and truthful job advertisements during the recruitment procedure, it has a positive influence on retaining new applicants. Those employers who are clear concerning the positive and negative facets of the job, as well as the challenges and anticipations, have higher chances to enroll and retain stronger applicants. In addition, companies can use socialization practices in order to cope with human resources employee retention difficulties. Socialization operations provided through a strategic onboarding and acculturation plans can assist new workers in becoming interposed in the organization and therefore more probable to retain. Such operations incorporate congregated and personalized educational practices, acts that provide employees with a possibility to get to know one another. This method is closely connected with training and development. The equipment of sufficient education and evolvement possibilities can increase turnover by making employees contented and well-positioned for future development and advancement opportunities. As a matter of fact, discontent with possible career evolvement is one of the major reasons why employees (35 percent) frequently feel prepossessed to look elsewhere. Nevertheless, if workers are not provided with possibilities to constantly advance their capacities, they are more likely to leave the position and the company itself. Those employees who get more education are less likely to go than those who get little or no education. Moreover, it is also important to remember that such issues as compensation and rewards are also important factors of improving retention ratios. Payment norms and standards together with overall satisfaction are mere frugal forecasters of an employee's resolution to leave the company. Nevertheless, companies are able to direct the market with a solid compensation and reward parcel due to the fact that at least 53 percent of employees frequently look elsewhere due to low compensation, bonuses and benefits. Finally, it is important to remember about employee engagement, as it is a significant factor for improving employee retention. Those employees who are content with their occupation, rejoin their work, and the company considers their profession and occupation to be more crucial, are proud of the organization and sense that their endowments are impressive are five times less probable to resign than those workers who were not engaged in the working process. Involved employees provide their organization with very important emulative advantages, incorporating greater productivity, effectiveness and efficiency, and lower employee turnover.
Conclusion
The current paper demonstrated that the issue of employee retention is closely connected with employee turnover. Typically, the level of company's turnover makes 80 percent, which means that employee retention is very low. The research demonstrated that the costs spent on new employees are very high. Therefore, the company should invest in improvements of employee retention, but not in new employees, who might never be as professional, as previous workers. The issue of employee retention can be solved with a help of improved compensation and rewards, socialization operations, and employee engagement. Sometimes, people are the most important company's assets; therefore, it is crucial to dedicate time to employee retention issues improvement.